The Path to 5G
The speed at which we surf and browse the internet, consume video and play games online is set to see a radical shift in the coming months and years ahead. With 5G networks being deployed around the world, new businesses are going to be created along with millions of jobs. However, the advantages and benefits we will soon see from 5G would not have been possible without its predecessor, 4G/LTE.
4G/LTE transformed the landscape of wireless in the US and around the world. Only launched in 2010, its impact since its introduction has been tremendous. It is essential to realize that 4G/LTE’s successes did not happen overnight. The advent of new apps and smartphones helped drive its popularity, but the gradual improvement of network coverage cemented its place as the platform of choice.
The Growth and Dominance of 4G
As 4G networks spread across the land, companies realized the benefits they provided. With fast 4G/LTE devices, linking these networks together along with innovative apps and services, consumers were able to accomplish tasks that had previously only been seen in the realm of Science Fiction.
The benefits were not only in the realm of services. The job market, too, was radically transformed, and in the US alone, the wireless industry helped to create 20.4 million jobs. This massive boost in productivity had a similar upside in revenue. Initial predictions for 4G/LTE were based on 3G trends. These trends predicted that by 2019, the GDP from wireless was expected to reach $441.8 billion –expected revenue growth of 126%. The fact is that this number was woefully inadequate. The actual number achieved was $690.5 billion – almost $250 billion more than what was predicted.
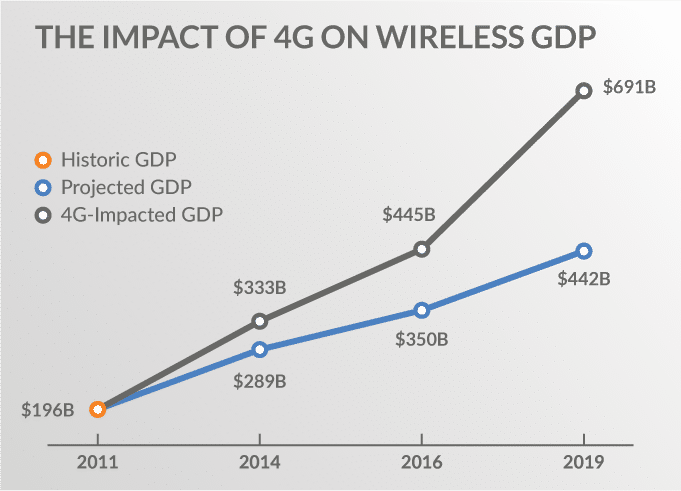
If you consider that during the same timeframe in the US, the overall GDP increased from $15.54 trillion to $21.43 trillion, you’ll understand that wireless alone accounted for nearly 10% of that growth.
How 5G Will Impact 4G/LTE
As 4G/LTE supplanted 3G on our devices as the network of choice, 5G will have a similar impact on individuals and economies around the world. However, the need for high speeds online is set to accelerate this shift at a pace never before seen, and by 2024, it is expected that there will be close to 2 billion 5G subscribers globally.
Now, this shift will not happen overnight – the 5G network is still being deployed in many economies around the world. In addition, many consumers will not be interested in purchasing a new 5G supported device – especially as the devices currently on the market are quite expensive. However, with Apple’s expected launch of a 5G device in the latter half of 2020, and positive word of mouth statements on 5G’s speeds, it will gradually start to become more mainstream.
Wireless and the Job Market
For a single industry, the impact of wireless over a short period cannot be discounted. In 2011, 3.7 million people were employed in wireless and related industries, which accounted for 2.4% of the employed population. However, only a short time later, the number had changed dramatically. By 2019 over 20 million jobs were dependent on wireless – a close to 14% increase in less than ten years.

The largest area of growth during this period of time was a sector that had not previously existed. The on-demand economy was formed to take advantage of the capabilities smartphones offered. This group included individuals involved in app development as well as individuals engaged in mobile hardware.
The creation of jobs with 4G was a huge benefit. Initial estimates were that each spectrum license would lead to 7,000 jobs was woefully low. In reality, the number of jobs created either directly or indirectly was closer to 524,000 jobs.
How 5G Will Impact Jobs
5G will have a similar impact on jobs and job creation to 4G/LTE. However, according to a report from the World Economic Forum, 5G will have an even more significant effect on the job market. While 4G/LTE saw 20 million jobs added to the economy, the expectation is that 5G will see that number increase to 22.3 million.
In the US, wireless contributes close to $500 billion in GDP and employees 4.7 million. 5G is set to change this number radically and will create close to 2-3 million new jobs. This is a growth of over 60 percent in the US alone.
Improved Speeds Lead to Greater Data Usage
The benefits of 4G/LTE were perhaps most apparent for consumers in terms of the speed they were able to realize. With 3G services, download speeds averaged 1.3 Mbits/second. This was sufficient for text searches and similar online activities. 4G/LTE radically transformed the landscape by offering speeds 31x faster at close to 41 Mbits/second.
With 4G/LTE latency was dramatically reduced from the 120 milliseconds on 3G to 60 milliseconds. This improvement in speed and latency led to a much richer experience for consumers with improved real-time communication and overall better reliability.
The benefits of the new network were not only realized by the public – but there were many business benefits also. Key improvements were with business productivity and cost savings. However, it bears pointing out that many companies polled pointed to Sales (57%) and Customer Services (40%) as the two departments that benefited the most from improvements in speed. With sales groups able to access information remotely at speed, and support organizations having more channels of communication available, it is easy to see why these teams benefited the most.
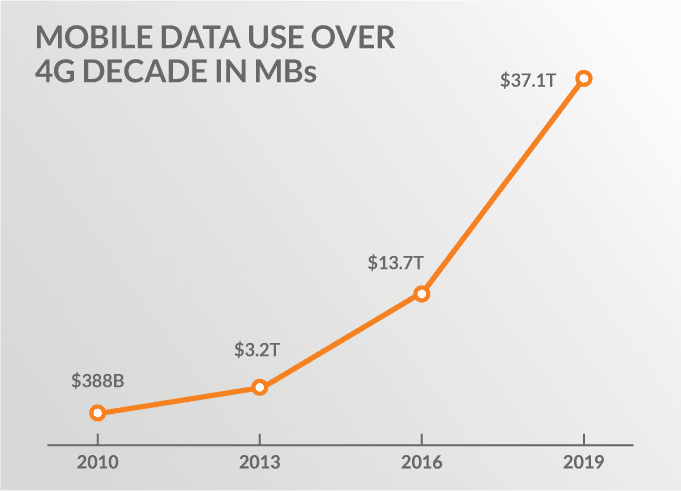
With the increasing speed available to all, usage dramatically increased. In theUS, with 3G, the amount of data used in 2010 was 388 billion MBs. Less than a decade later, this number had increased 96 times, and the amount of data used by Americans surpassed 37 trillion MBs. This massive increase was driven by apps and mobile broadband.
With 3G networks, smartphone users started to explore the capabilities of apps. In those early days, a smartphone consumed about 360 MB/month. With more and more apps coming onto the market and user familiarity growing, the amount of data used monthly reached an average of 9.2 GB/month by 2019.
Data Usage With 5G
The growth we have seen over the past decade in terms of data usage is the tip of the iceberg. South Korea is a very useful forerunner when it comes to mobile phone technology. In fact, they turned on their first 5G network in 2019, and since its introduction, it has rolled out to 85 cities nationwide. Since its launch, it has skyrocketed in popularity with 1 million subscribers utilizing the service after 69 days and is currently growing at an average rate of 17,000 new consumers per day.
The data from South Korea can help us understand what to expect worldwide as 5G networks continue to roll out globally. On 4G networks, 4G/LTE consumers in South Korea averaged 9GB of monthly data usage. Those same subscribers are now consuming more than double that amount at 18.3GB/mo. This increase is driven through the speed available, but also new services available on 5G like AR/VR content that was not previously available on 4G/LTE.
Price Drops but Value Rises
Fortunately, with 4G/LTE, despite the growth in demand and overall usage, an upswing in price did not happen. In fact, over the past decade, prices have actually decreased. In 2010 the average cost for a US consumer for an unlimited voice, data, and text plan were in the range of $114/line per month. By 2019, that same plan had shrunk in cost by 43% to an average price per line of $65/month. This difference saved the average consumer about $588/year or a massive $130 billion/year for US consumers combined.
This change in price can be seen even more in the price/MB paid by consumers. In 2011, consumers spent $0.20/MB for data. However, by 2019, this cost had decreased to $0.005/MB – this was a change of 98%. Thankfully for consumers, this decrease in price was not matched by a reduction in service. In fact, it was the exact opposite.
Over the course of the decade, 4G/LTE helped drive improved connectivity to millions of low-income Americans and helped communities find new ways of connecting. Many Americans now depend on wireless solely and have moved away from standard telephone services.
5G Pricing a Question
While price reductions have been seen over the course of time for 4G/LTE, at this time, price reductions for 5G still up in the air. Some jurisdictions around the world have mandated a decrease in cost in 2 years; however, whether or not this will happen is up for debate.
How 4G/LTE was used and how 5G will be used are very different. It is quite likely that individual services will be lower, but as 5G gradually takes a more central place, the overall cost will be higher. At the current time, 5G usage requires an investment into new hardware. As this hardware comes down in price, it is expected that service plans will match 4G/LTE.
4G/LTE and Business
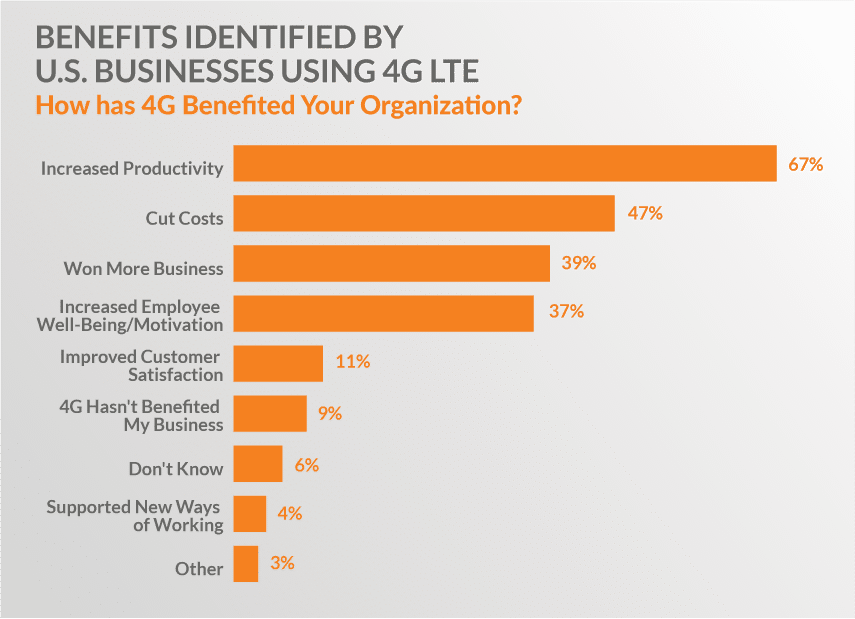
Improved speed and data transfer impacted business organizations in a variety of ways. Perhaps most importantly, it improved their flexibility, which had a direct impact on their agility and decision-making processes. EE, a mobile phone operator based in the UK, conducted a survey of US businesses, which pointed to a 67% productivity gain due to the implementation of 4G/LTE. In addition, 39% of these organizations indicated that 4G/LTE had improved their ability to win new business, and an additional 47% talked about the benefits of saving costs.
The implementation of 4G/LTE networks has let companies engage with their workforce in ways not previously available. With 4G/LTE connectivity, employees are able to work remotely and are not forced to log into a WiFi connection. These benefits also accrue to remote monitoring and repair of equipment in the field, helping save the company and the employee, time, and money.
Customer Experience Improvements
From a business point of view, 4G/LTE improves the customer experience in multiple ways. With the ability it grants to letting staff work remotely, teams are better able to respond to customer inquiries from any mobile device, improving the overall service level provided.
eCommerce Improvements
Sales are the lifeblood of any business, and today’s consumers continue to move towards eCommerce as a preferred channel in ever more significant numbers. With 4G/LTE, consumers are able to browse for items and research information regardless of where they are located. The increasing number of smartphones available worldwide is helping to push this trend ever higher and further decreasing shopper’s dependence on brick-and-mortar establishments.
How 5G Will Impact Business
The impact of 5G on the business world is expected to be nothing less than revolutionary. While 4G/LTE improved the overall customer experience and helped launch eCommerce, 5G is going to drive smart cities and autonomous vehicles.
The transition will not happen overnight – 4G/LTE is still popular and continues to grow. In fact, it is expected to grow to 56% by 2025. While consumers want higher speeds, they do not want to pay for expensive plans or devices, which is why the initial drivers of growth for 5G are going to be business. The key drivers of this growth are the low latency and fast speeds 5G offers. These benefits will help create autonomous factories, as has already been seen in China. The Chinese example saw a factory reduce its workforce by 90% but increase productivity by 250% through automation.
Automation is only one area where 5G will be making massive inroads. Newer technologies like Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are also set to explode in popularity and growth. 5G adoption around the world will not be uniform, however. Developed Asian countries continue to lead the way, followed by North America. Europe and other jurisdictions continue to lag behind.
The 5G Future
Each new generation of technology has brought improvements with faster and more reliable connections. Since 2010 and the launch of 4G/LTE, wireless services have transformed the way people play, work, and live. Currently, in the US alone, wireless supports 20 million jobs and helps contribute $700 billion annually to the economy. However, while these changes have been astronomical, what is coming in soon will dwarf them.
5G is gradually being rolled out around the world. 4G/LTE was a significant improvement over 3G in terms of speed and latency. However, 4G/LTE is reaching its limits in terms of the amount of data it can transfer at speed due to the congestion on the networks. 5G networks are set to change this by increasing the amount of available spectrum mobile operators have access to.

While a full deployment of 5G will take years, higher speeds and improved connectivity will see 5G become the catalyst for connectivity between humans and machines. A reduction in latency to one or two milliseconds will dramatically improve what is possible in terms of remote operation. In addition, 5G’s improved speeds will help drive the creation of smart cities along with self-driving autonomous vehicles.
Accessing 5G networks will require new hardware as devices built to support 4G/LTE networks will be unable to access the more modern networks. While 5G is already available in some larger metropolitan locations, its full rollout is only beginning. However, it is expected that 5G will be available throughout the country by 2022.
It is essential to understand that many web services we now take for granted did not exist prior to 4G/LTE. It is expected that the growth and expansion of 5G will have a similar impact on society and business. No one can predict what the future will hold, but as 5G grows and matures, the potential it offers is almost limitless.




